Thanks to Tonga’s ccTLD, the U.S. Supreme Court and other institutions…
Information security headlines usually focus on data breaches, cyber attacks, vulnerabilities, and other threats or events, and these threats or events are usually related to human error.
Drink it every day It has been decided to correct this balance by focusing on some positive news reports, highlighting the commendable actions of cybersecurity professionals and organizations, developers and open source maintainers, and even journalists and judges.
(We did not include any breakthrough security research that occurred during 2021-we will leave it to Portswigger researcher James Kettle’s upcoming annual round of top cyber hacking techniques, which is a follow-up to the 2020 round.)
The first website dedicated to revealing vulnerabilities in malware
The beginning of the year was the launch of a groundbreaking database that can index exploit codes for security vulnerabilities in malware.
Founder John Page told Drink it every day Repositories may be “useful for incident response teams to eradicate malware without touching the machine” and “may eventually lead to conflicts between malware and malware, who knows.”
Similarly, Abuse.ch launched a platform in March for sharing and requesting indicators of compromise (IoC) related to various malware strains.
SolarWinds eliminates the complacency of the U.S. government over cybersecurity
The SolarWinds attack, which attacked federal agencies and blue-chip companies at the end of 2020, sounded a wake-up call for the White House.
An executive order signed by the newly elected President Biden in May set the tone for a busy year in cyber security.
Follow new rules for reporting ransomware payments and protecting critical transportation infrastructure; radically reform the federal government’s software procurement practices; a series of 60-day “sprints” aimed at establishing cyber resilience; US federal agencies plan to establish a system to quickly patch Hundreds of known and exploited flaws; “Hack the DHS” bug bounty program; and the first ever vulnerability disclosure program for federal civil agencies.
Chief Scientist Aaron Portnoy said: “The government is taking good steps to make it public, launch initiatives, hire new CISA directors, and start working with other countries on the actions we will take on this. Dialogue.” Attack surface management expert Randori told Drink it every day In July.
do not miss it A few weeks after the high-profile supply chain attack, multiple new flaws were discovered in the SolarWinds software
Research on the Liberation Security of the U.S. Supreme Court
After the U.S. Supreme Court made its ruling in June, it decisively tilted the judicial scale to favor ethical hackers. The ruling effectively reduced the “Unauthorized Access” under the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA). Scope.
Information security experts have long criticized the CFAA’s ambiguity about well-intentioned hacking, which has a chilling effect on security research.
This ruling should reassure the civic-conscious journalist that he threatened to take legal action after Missouri Governor Mike Parson responsibly reported a serious loophole on the state government website. To the widespread ridicule.
Nevertheless, many people believe that the law dates back to 1986 and should be completely replaced.
Following the industry-led movement, the United Kingdom announced in May that it would review its equivalent legislation, the Computer Abuse Act.
OWASP Top 10 should be refreshed long ago
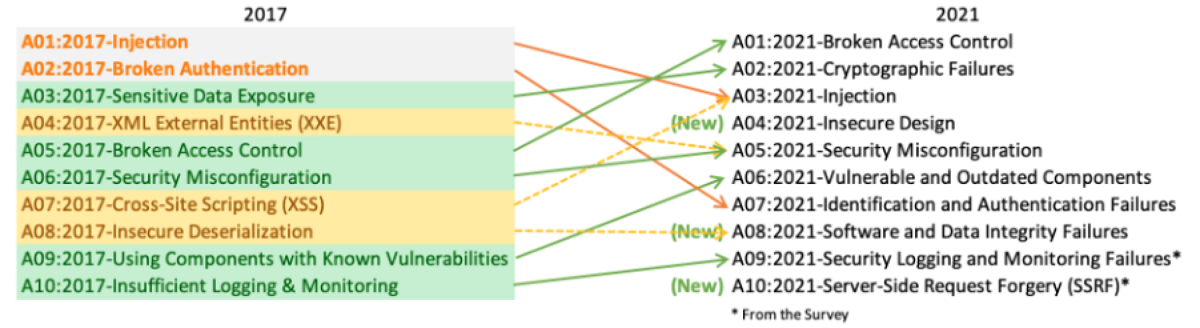
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) updated its top 10 web application threat categories in September for the first time since 2017.
Three new categories-“insecure design”, “software and data integrity failure”, and “server-side request forgery (SSRF)” attacks-and the name changes of several other categories have been added.
Tom Eston, Bishop Fox’s application security practice director, said that the transformation reflects the “shift to the left” of the software industry, focusing more on security design and architecture and threat modeling. Drink it every day.
 Top 10 OWASP updated
Top 10 OWASP updated
HTTPS is finally almost everywhere
The HTTPS Everywhere browser extension announced in September was deprecated. According to its developer, the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), this is a case of “mission completion”.
The plug-in was launched in 2010 and automatically switches the web connection from HTTP to HTTPS (if the latter is available) and accumulates More than two million users In the absence of similar built-in features in popular browsers.
With the widespread adoption of HTTPS, open source extensions will enter “maintenance mode” in 2022, and after Google and Firefox enforce HTTPS by default, the plug-in is basically redundant.
These changes are part of the security development of many other browsers Drink it every day All of 2021 will be highly anticipated.
Google provides shields against surveillance
In October, Google used its vast resources to protect journalists, elected officials, and human rights activists from surveillance, persecution, and imprisonment.
The tech giant worked with human rights and democracy organizations to distribute free physical security keys to more than 10,000 state-sponsored hackers at high risk under its Advanced Protection Program (APP).
Wrong recording of bounty payouts proves value for money
The record bug bounty spending in October clearly shows that crowdsourcing security can bring a substantial return on investment.
Although the $2 million that was paid by blockchain technology company Polygon to ethical hacker Gerhard Wagner for the “double-spend” vulnerability, the money is jaw-dropping, but this number should be compared with the possible avoidable losses.
This flaw actually means that attackers can increase their cryptocurrency withdrawals by up to 233 times, for example, US$3.8 million may become US$850 million.
read Lessons learned: How serious vulnerabilities in the core set of OWASP ModSecurity rules trigger much-needed changes
Admit mistakes and learn from them
A serious, long-standing vulnerability in the OWASP ModSecurity Core Rule Set (CRS) was a “sensation” for the maintainers of the project when it was discovered, OWASP CRS co-leader Christian Folini told Drink it every day November.
Now patched, the critical, complete rule set bypass has prompted the ModSec team to implement new practices, guidelines, and bug bounty programs to further protect the technology.
It is commendable that Folini assumed responsibility for the two mistakes that his team inadvertently introduced after taking over this dormant project in 2016, and was determined to “see it as an opportunity for growth and development”.
Quick fix
As the time between vulnerability disclosure and wild exploitation shortens to days or even hours, the credit goes to vendors, maintainers, and end users who quickly released or applied patches in 2021.
This includes the Tonga country code top-level domain (ccTLD) registrar Tonic, which patched a serious vulnerability in its website in less than 24 hours in December to open up potential attacks on domain names operated by Google, Amazon, and Amazon Closed the door. Many others.
The maintainers of Apache Log4j, the ubiquitous Java logging library, have also done a good job because they rushed to release patches for the potentially destructive Log4Shell vulnerability in Dacember, and because of its transparency in communicating high-severity security vulnerabilities, virtual machine.
After two sharp-eyed Irish citizens discovered in July that there was a spelling error in the URL of Ireland’s new Covid-19 recovery certificate portal and registered a correctly spelled domain, they rejected the golden phishing opportunity of scammers, which is also commendable.
read Swig Security Review 2021-Part One



