Apple recently fixed a security vulnerability in the macOS operating system. Attackers may use the vulnerability “simple and reliable” to bypass “numerous basic macOS security mechanisms” and run arbitrary code.
Security Researcher Patrick Wardle detailed This discovery was discovered in a series of tweets on Thursday.Tracked as CVE-2021-30853 (CVSS score: 5.5), the problem is related to scenarios that rogue macOS applications may circumvent Watchmen Check to make sure that only trusted applications can run, and they have passed a file called “Application notarization.”
The iPhone manufacturer believes that Box’s Gordon Long has reported the defect and said Solved the weakness As part of the macOS 11.6 update officially released on September 20, 2021, improved checks.
“Such errors usually have a particular impact on daily users of macOS, because they provide adware and malware authors with a way to circumvent macOS security mechanisms…otherwise mechanisms that prevent infection attempts,” Wardle Say In the technical report of the defect.
Specifically, the vulnerability not only bypasses Gatekeeper, but also File isolation As well as macOS’s notarization requirements, it effectively allows a seemingly harmless PDF file to harm the entire system just by opening it.According to Wardle, the root cause of this problem is that unsigned, unnotarized script-based applications can no Clearly specify one Interpreters, Leading to a complete bypass.
It’s worth noting that a Shebang Interpreter instructions-such as #!/bin/sh or #!/bin/bash-are usually used to parse and interpret shell programs. But in this kind of edge attack, the attacker can make an application to merge the shebang line without providing an interpreter (ie #!) and still let the underlying operating system start the script without issuing any alarms.
This is because “macOS will (re)attempt to execute failed [‘interpreter-less’ script-based app] Wardle explained that after initially unsuccessful, through the shell (‘/bin/sh’)”.
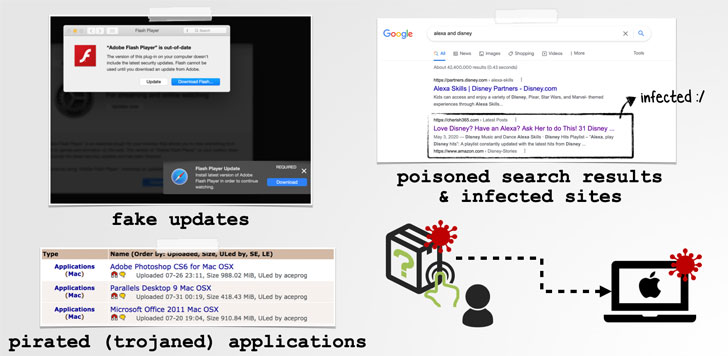
In other words, an attacker can exploit this vulnerability by tricking the target into opening a rogue application, which can be disguised as a Trojan horse version of a legitimate application such as Adobe Flash Player update or Microsoft Office, and these applications can Through what is known as search poisoning, the attacker artificially increases the search engine rankings of websites hosting their malware in order to lure potential victims.
This is not the first time a defect has been discovered in the Gatekeeper process. In early April of this year, Apple quickly patched a zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2021-30657) that was actively exploited at the time, which could bypass all security protection measures, allowing unapproved software to run on the Mac.
Then in October, Microsoft disclosed a vulnerability called “Shrootless” (CVE-2021-30892), which can be used to perform arbitrary operations, elevate root privileges, and install rootkits on infected devices.Apple Say As part of the security update pushed on October 26, 2021, it fixes the issue with additional restrictions.





